Black box Testing
What is Black box Testing?
Black-box testing is a method of software testing that examines the functionality of an application based on the specifications. It is also known as Specifications based testing. Independent Testing Team usually performs this type of testing during the software testing life cycle.
This method of test can be applied to each and every level of software testing such as unit, integration, system and acceptance testing.
Black box testing is a type of software testing in which the functionality of the software is not known. The testing is done without the internal knowledge of the products..
Generic steps of black box testing
- The black box test is based on the specification of requirements, so it is examined in the beginning.
- In the second step, the tester creates a positive test scenario and an adverse test scenario by selecting valid and invalid input values to check that the software is processing them correctly or incorrectly.
- In the third step, the tester develops various test cases such as decision table, all pairs test, equivalent division, error estimation, cause-effect graph, etc.
- The fourth phase includes the execution of all test cases.
- In the fifth step, the tester compares the expected output against the actual output.
- In the sixth and final step, if there is any flaw in the software, then it is cured and tested again.
Black box testing can be done in the following ways:
1. Syntax-Driven Testing – This type of testing is applied to systems that can be syntactically represented by some language. For example- compilers, language that can be represented by a context-free grammar. In this, the test cases are generated so that each grammar rule is used at least once.
2. Equivalence partitioning – It is often seen that many types of inputs work similarly so instead of giving all of them separately we can group them and test only one input of each group. The idea is to partition the input domain of the system into several equivalence classes such that each member of the class works similarly, i.e., if a test case in one class results in some error, other members of the class would also result in the same error.
The technique involves two steps:
- Identification of equivalence class – Partition any input domain into a minimum of two sets: valid values and invalid values. For example, if the valid range is 0 to 100 then select one valid input like 49 and one invalid like 104.
- Generating test cases – (i) To each valid and invalid class of input assign a unique identification number. (ii) Write a test case covering all valid and invalid test cases considering that no two invalid inputs mask each other. To calculate the square root of a number, the equivalence classes will be: (a) Valid inputs:
- The whole number which is a perfect square- output will be an integer.
- The whole number which is not a perfect square- output will be a decimal number.
- Positive decimals
- Negative numbers(integer or decimal).
- Characters other than numbers like “a”,”!”,”;”, etc.
3. Boundary value analysis – Boundaries are very good places for errors to occur. Hence if test cases are designed for boundary values of the input domain then the efficiency of testing improves and the probability of finding errors also increases. For example – If the valid range is 10 to 100 then test for 10,100 also apart from valid and invalid inputs.
4. Cause effect Graphing – This technique establishes a relationship between logical input called causes with corresponding actions called the effect. The causes and effects are represented using Boolean graphs. The following steps are followed:
- Identify inputs (causes) and outputs (effect).
- Develop a cause-effect graph.
- Transform the graph into a decision table.
- Convert decision table rules to test cases.
For example, in the following cause-effect graph:
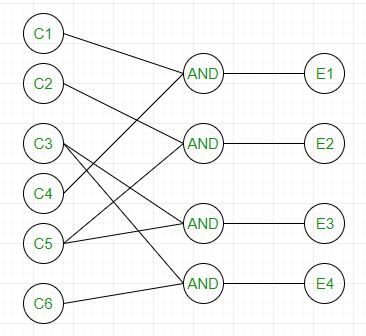
It can be converted into a decision table like:
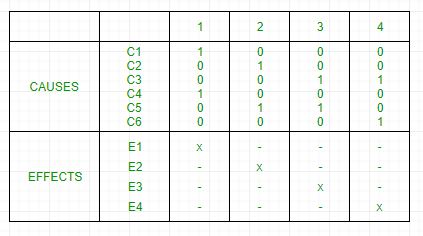
Each column corresponds to a rule which will become a test case for testing. So there will be 4 test cases.
5. Requirement-based testing – It includes validating the requirements given in the SRS of a software system.
6. Compatibility testing – The test case result not only depends on the product but is also on the infrastructure for delivering functionality. When the infrastructure parameters are changed it is still expected to work properly. Some parameters that generally affect the compatibility of software are:
- Processor (Pentium 3, Pentium 4) and several processors.
- Architecture and characteristics of machine (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Back-end components such as database servers.
- Operating System (Windows, Linux, etc).
Black Box Testing Type
The following are the several categories of black box testing:
- Functional Testing
- Regression Testing
- Nonfunctional Testing (NFT)
Functional Testing: It determines the system’s software functional requirements.
Regression Testing: It ensures that the newly added code is compatible with the existing code. In other words, a new software update has no impact on the functionality of the software. This is carried out after a system maintenance operation and upgrades.
Nonfunctional Testing: Nonfunctional testing is also known as NFT. This testing is not functional testing of software. It focuses on the software’s performance, usability, and scalability.
Tools Used for Black Box Testing:
- Appium
- Selenium
- Microsoft Coded UI
- Applitools
- HP QTP.
Advantages of Black Box Testing:
- The tester does not need to have more functional knowledge or programming skills to implement the Black Box Testing.
- It is efficient for implementing the tests in the larger system.
- Tests are executed from the user’s or client’s point of view.
- Test cases are easily reproducible.
- It is used in finding the ambiguity and contradictions in the functional specifications.
Disadvantages of Black Box Testing:
- There is a possibility of repeating the same tests while implementing the testing process.
- Without clear functional specifications, test cases are difficult to implement.
- It is difficult to execute the test cases because of complex inputs at different stages of testing.
- Sometimes, the reason for the test failure cannot be detected.
- Some programs in the application are not tested.
- It does not reveal the errors in the control structure.
- Working with a large sample space of inputs can be exhaustive and consumes a lot of time.
Techniques Used in Black Box Testing
| Decision Table Technique | Decision Table Technique is a systematic approach where various input combinations and their respective system behavior are captured in a tabular form. It is appropriate for the functions that have a logical relationship between two and more than two inputs. |
| Boundary Value Technique | Boundary Value Technique is used to test boundary values, boundary values are those that contain the upper and lower limit of a variable. It tests, while entering boundary value whether the software is producing correct output or not. |
| State Transition Technique | State Transition Technique is used to capture the behavior of the software application when different input values are given to the same function. This applies to those types of applications that provide the specific number of attempts to access the application. |
| All-pair Testing Technique | All-pair testing Technique is used to test all the possible discrete combinations of values. This combinational method is used for testing the application that uses checkbox input, radio button input, list box, text box, etc. |
| Cause-Effect Technique | Cause-Effect Technique underlines the relationship between a given result and all the factors affecting the result.It is based on a collection of requirements. |
| Equivalence Partitioning Technique | Equivalence partitioning is a technique of software testing in which input data divided into partitions of valid and invalid values, and it is mandatory that all partitions must exhibit the same behavior. |
| Error Guessing Technique | Error guessing is a technique in which there is no specific method for identifying the error. It is based on the experience of the test analyst, where the tester uses the experience to guess the problematic areas of the software. |
| Use Case Technique | Use case Technique used to identify the test cases from the beginning to the end of the system as per the usage of the system. By using this technique, the test team creates a test scenario that can exercise the entire software based on the functionality of each function from start to end. |